A system is said to be in thermodynamic equilibrium, if it satisfies the following requirements of equilibrium.
→ Mechanical Equilibrium
→ Thermal Equilibrium
→ Chemical Equilibrium
→ Electrical Equilibrium
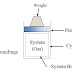
⏩ Mechanical Equilibrium: A system is said to be in mechanical equilibrium, when there is no unbalanced forces acting on any parts of the system or the system as whole. For a system to be mechanical equilibrium there should be no pressure gradient within the system.
⏩ Thermal Equilibrium: A system is said to be in thermal equilibrium, when there is no temperature difference between the parts of the system or between the system and surroundings.
⏩ Chemical Equilibrium: A system is said to be in chemical equilibrium, when there is no chemical reaction within the system and also there is no movement of any chemical constituent from one part of the system to the other.
⏩ Electrical Equilibrium: A system is said to be in mechanical equilibrium, when there is no electrical potential gradient presents on any parts of the system or the system as
whole.
When all the conditions of mechanical, thermal, chemical & electrical are satisfied, then the system is said to be in thermodynamic equilibrium.










No comments:
Post a Comment